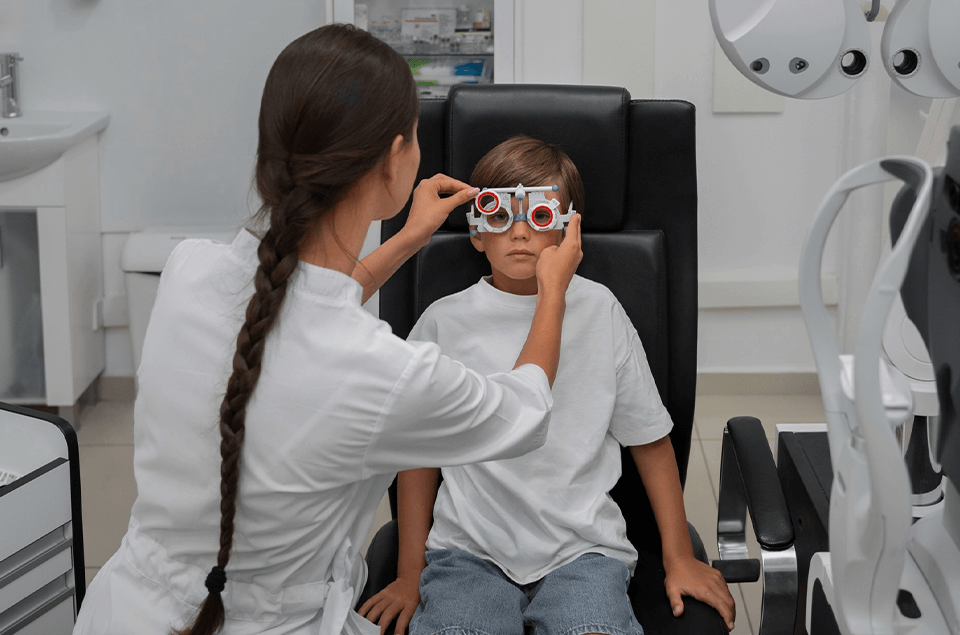
What Does Low Vision Mean?
Causes of Low Vision :
Low vision is a term used to describe a visual impairment that cannot be fully corrected through traditional means such as contact lenses, eyeglasses, medications, or surgical procedures. This condition can significantly impact an individual's
ability to perform everyday activities, from reading and driving to recognizing faces and navigating familiar environments. While low vision presents challenges, many individuals can benefit from specialised visual aids and adaptive
strategies, empowering them to enhance their remaining sight and maintain independence in their daily lives.

Eye Injuries: Accidents and trauma to the eye can cause severe damage, leading to lasting visual impairment. These injuries may affect various parts of the eye, impacting overall vision.

Macular Degeneration: Both age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and hereditary forms can severely affect the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp vision. This condition often results in difficulty with
tasks such as reading and recognizing faces.

Glaucoma: Often referred to as the "silent thief of sight," glaucoma involves a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve, typically due to increased intraocular pressure. Early detection and treatment are crucial to
prevent significant vision loss.

Albinism: This genetic condition leads to a lack of pigmentation in the eyes, skin, and hair, which can cause various visual difficulties, including sensitivity to light, reduced visual acuity, and nystagmus (involuntary eye
movement).